Welcome to Ms. Stephens 10th Grade Biology Class!
We are learning about Proportion or Frequency of Gene Expression!
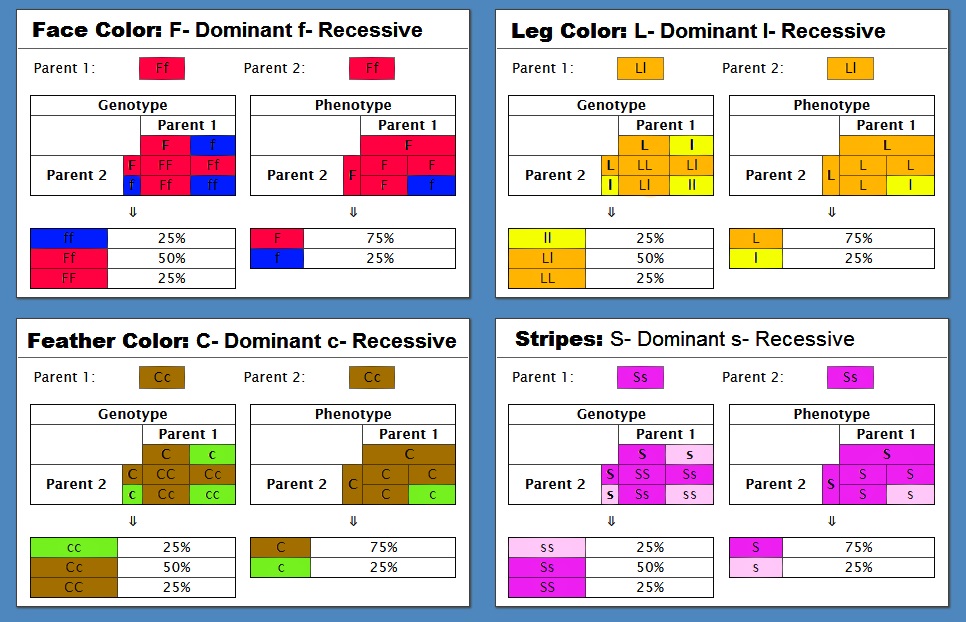
Phenotypic Expression of Turkeys:
- Face Color: Dominant (F) is red while the Recessive,(f), is blue.
- Leg Color: Dominant (L) is orange, and Recessive (l) is yellow.
- Feather Color: Dominant (C) makes the turkey brown, while Recessive (c) makes them colorful!
- Stripes: Dominant (S) signifies the presence of stripes, while the Recessive (s) means the turkey has no stripes.
Think-Pair-Share Activity!
Take some time to work together on the Think Pair Share Turkey Genetics coloring activity. If your phenotype contains capital letters then the alleles/ traits have a dominant expression. Likewise, if the phenotype contains lower case letters, it has a recessive expression!
Examples:
- The phenotype FLCs expresses the dominant traits for Face Color, Leg Color, and Feather Color. The Face color would be Red, the Leg Color would be orange, and the Feather Color would be Brown since these are all dominant. The trait for Stripes, s, is recessive making the turkey absent of stripes!
- The phenotype fLCS has a recessive trait for Face Color, so the face would be Blue. We know the Leg Color, Feather Color, and the Stripes are all dominant characteristics, so this turkey has orange legs, brown feathers, and stripes!
- The phenotype flcS expresses the recessive trait for Face Color, blue. The Leg Color is also recessive, so they will be Yellow! Even more interesting, the Feather Color is also recessive; this makes the turkey Colorful instead of the dominant Brown!



Work together on your Coloring Sheet and decide your turkey’s physical characteristics!
Take some time to work together on the Think Pair Share Turkey Genetics coloring activity. If your phenotype contains capital letters then the alleles/ traits have a dominant expression. Likewise, if the phenotype contains lower case letters, it has a recessive expression!
- Do you know some of their Possible genotypes? If a phenotype is dominant, it can either be (DD) or (Dd) and still express the dominant characteristic. If a phenotype is recessive, it can ONLY be (dd)!
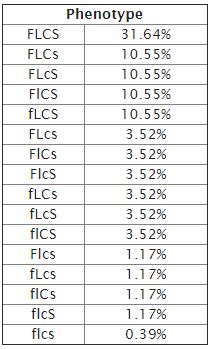
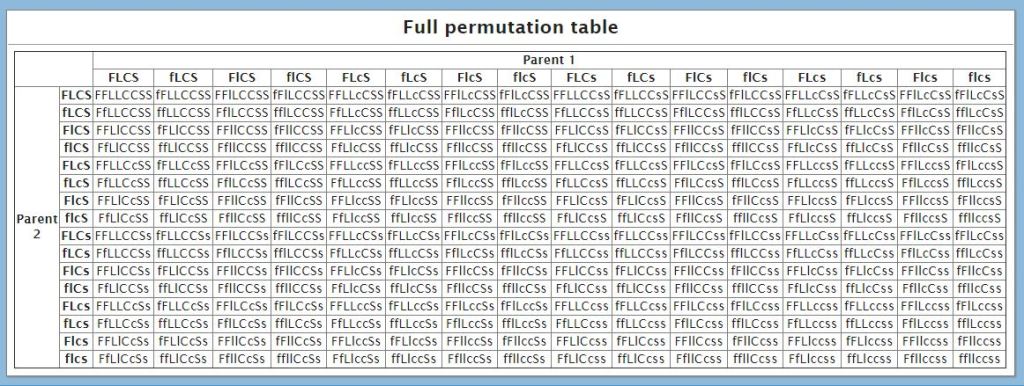
This is the list of the ration or proportion of the distribution of different Phenotypes illustrated in the room from the permutation table below!
These result from the breeding of two parents with the same heterozygous genotype: FfLlCcSs x FfLlCcSs. 31.64% of the offspring exhibit the same traits as the parents with either a FfLlCcSs or FFLLCCSS genotype, while only 0.39% exhibit a homozygous recessive genotype ffllccss out of the possible 256 offspring!!
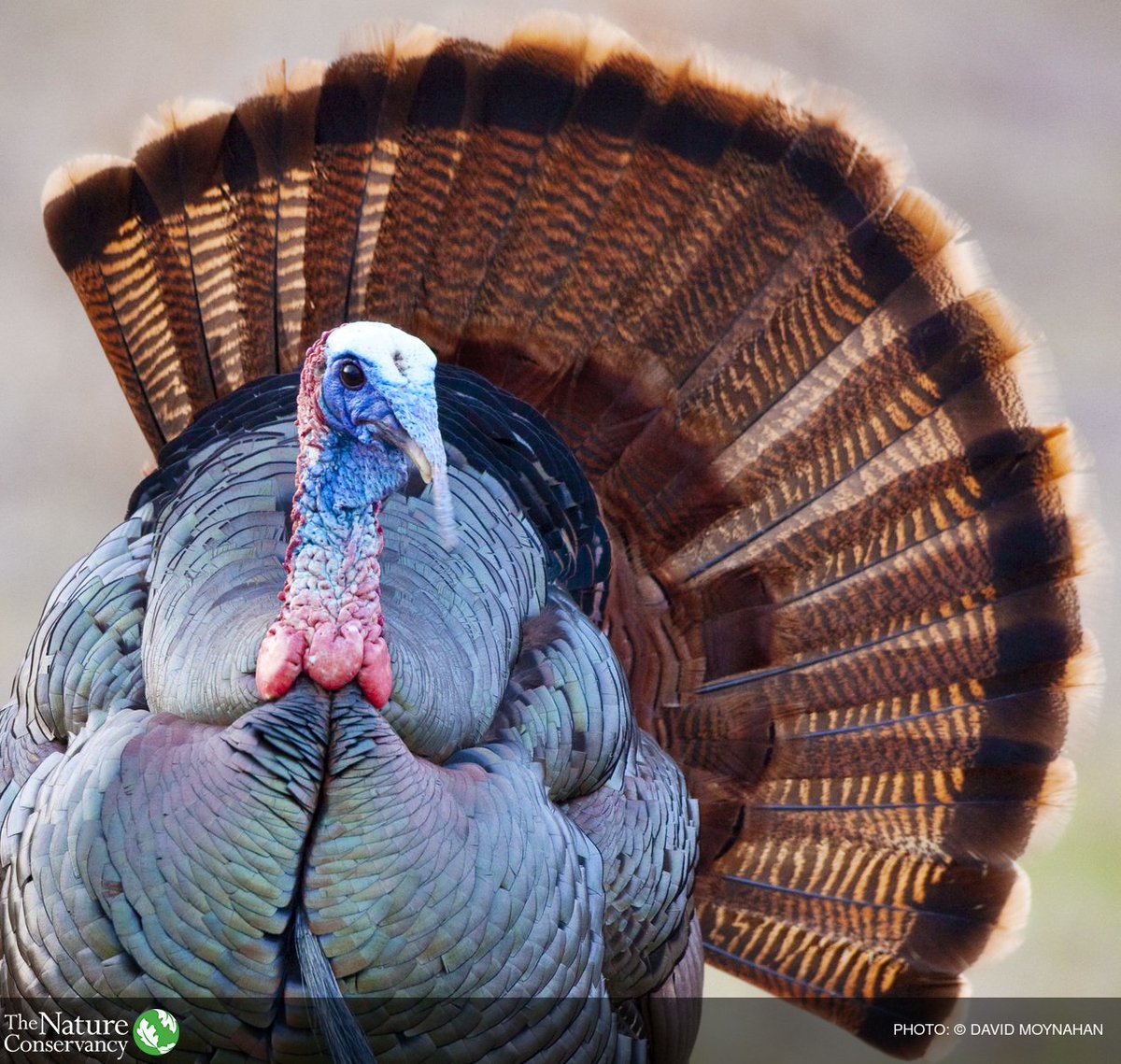
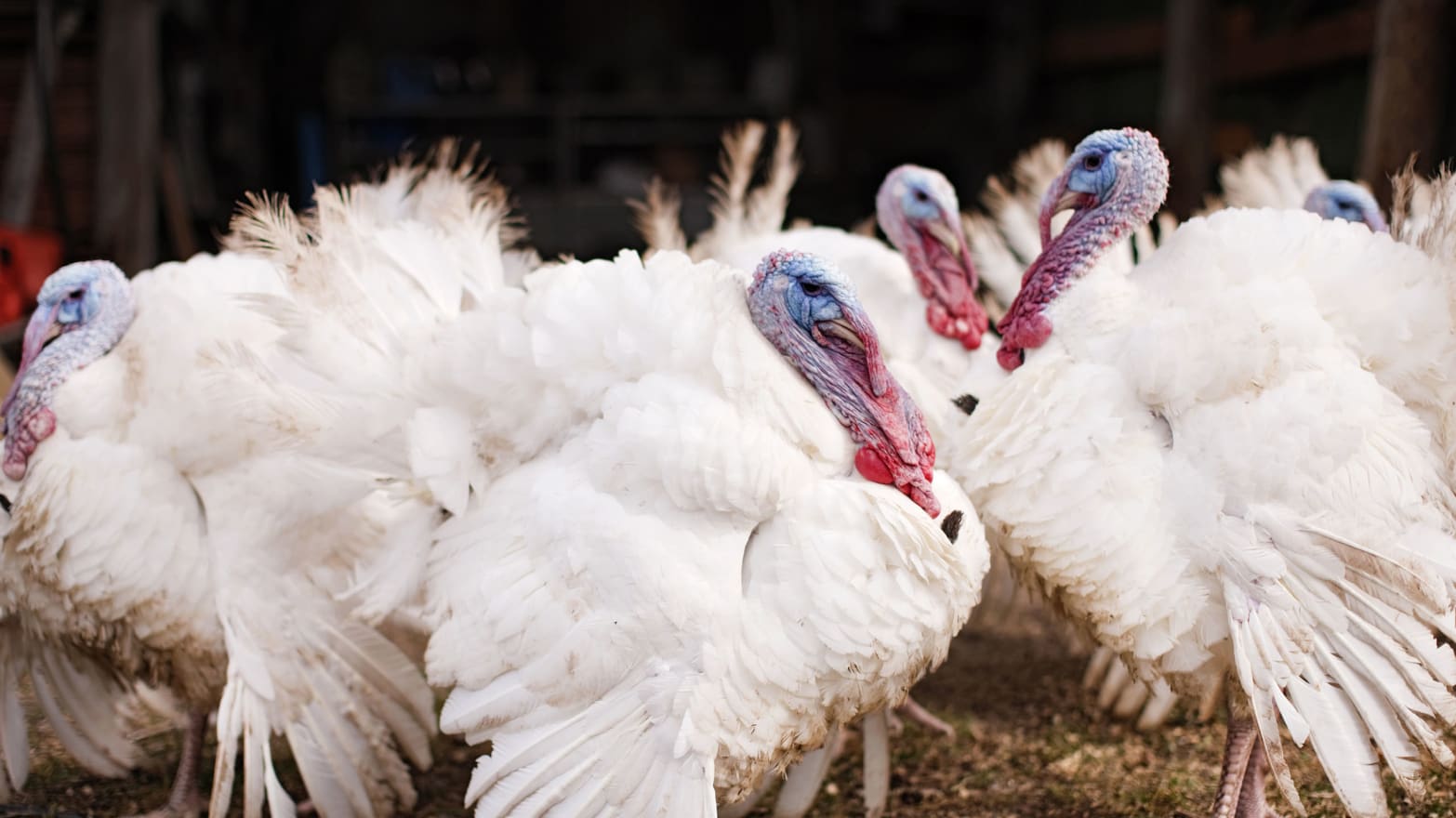
Here are some real-life turkey breeds that express many differences in their phenotypes! !

*fLCs has no stripes because s is recessive
*fLCS has stripes present because S is dominant






Thank you for your participation in class today! I hope you all have a wonderful Thanksgiving Holiday! When we come back to school from the break, we will pick up where we left off in the chapter by studying the Galapagos Island Finches. Then, we will of go more in depth with genetic frequency proportion through studying the Hardy Weinberg effect!